PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE (PCT)
● `color{violet}("PCT")` is lined by `color{brown}("simple cuboidal brush border epithelium")` which increases the `color{violet}("surface area")` for `color{violet}("reabsorption.")`
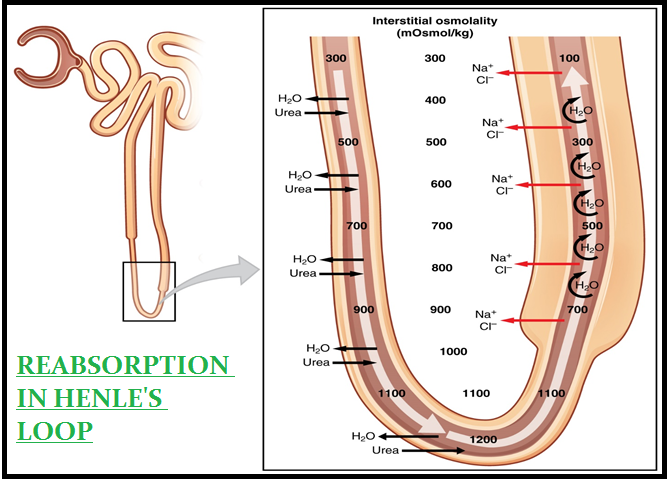
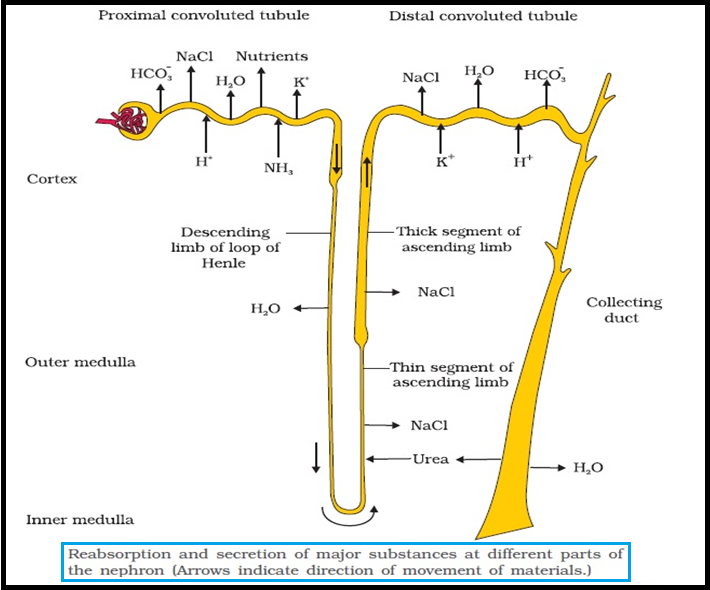
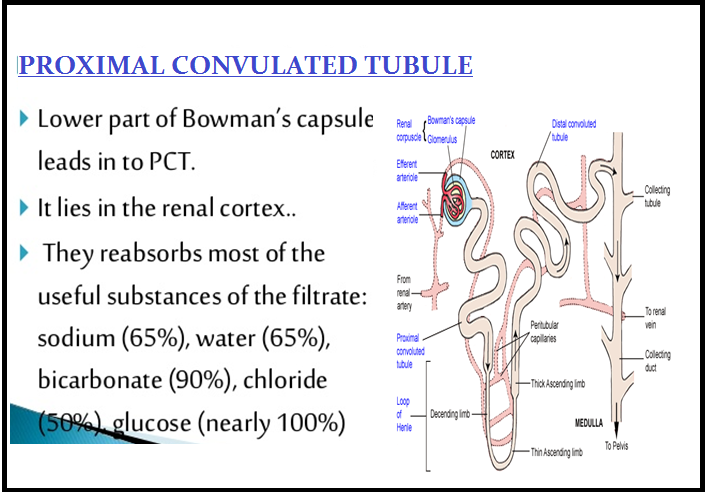
● Nearly all of the `color{violet}("essential nutrients,")` and `color{brown}("70-80 %)` of `color{violet}("electrolytes and water")` are reabsorbed by this segment.
● PCT also helps to maintain the pH and `color{violet}("ionic balance")` of the body fluids by selective secretion of `color{violet}("hydrogen ions, ammonia and potassium ions")` into the filtrate and by absorption of `color{violet}(HCO_3^(–))` from it
● Nearly all of the `color{violet}("essential nutrients,")` and `color{brown}("70-80 %)` of `color{violet}("electrolytes and water")` are reabsorbed by this segment.
● PCT also helps to maintain the pH and `color{violet}("ionic balance")` of the body fluids by selective secretion of `color{violet}("hydrogen ions, ammonia and potassium ions")` into the filtrate and by absorption of `color{violet}(HCO_3^(–))` from it